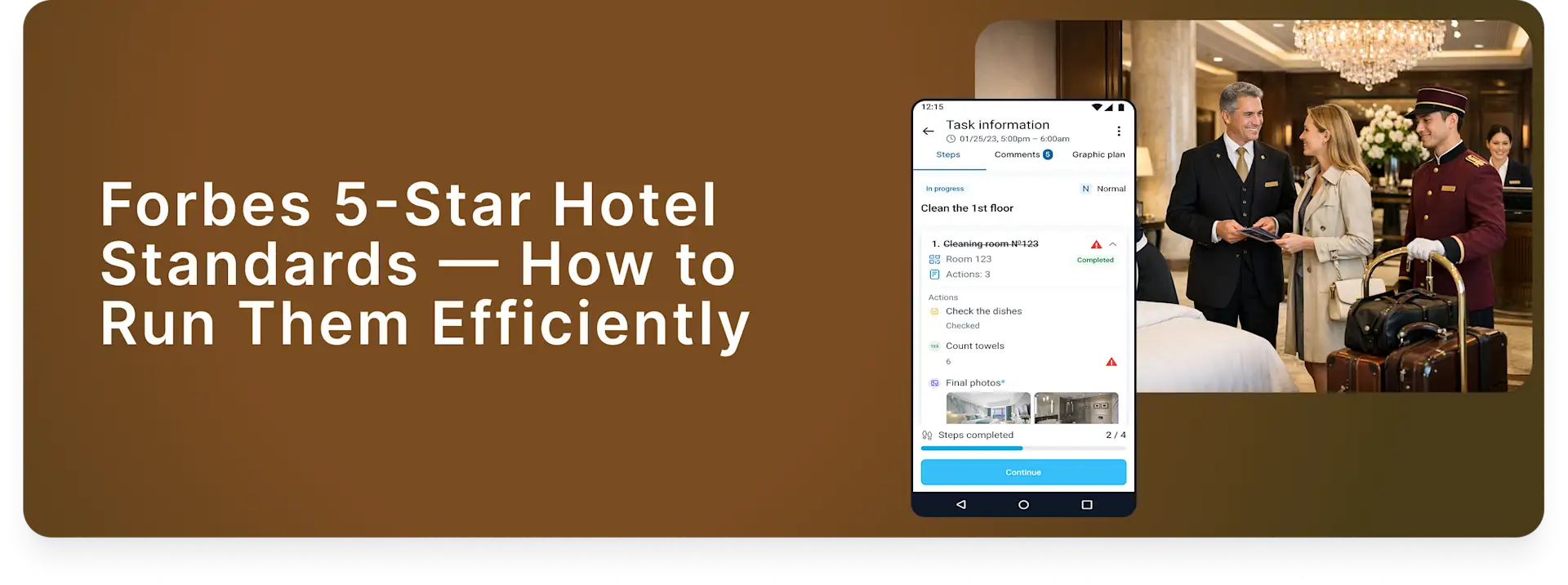
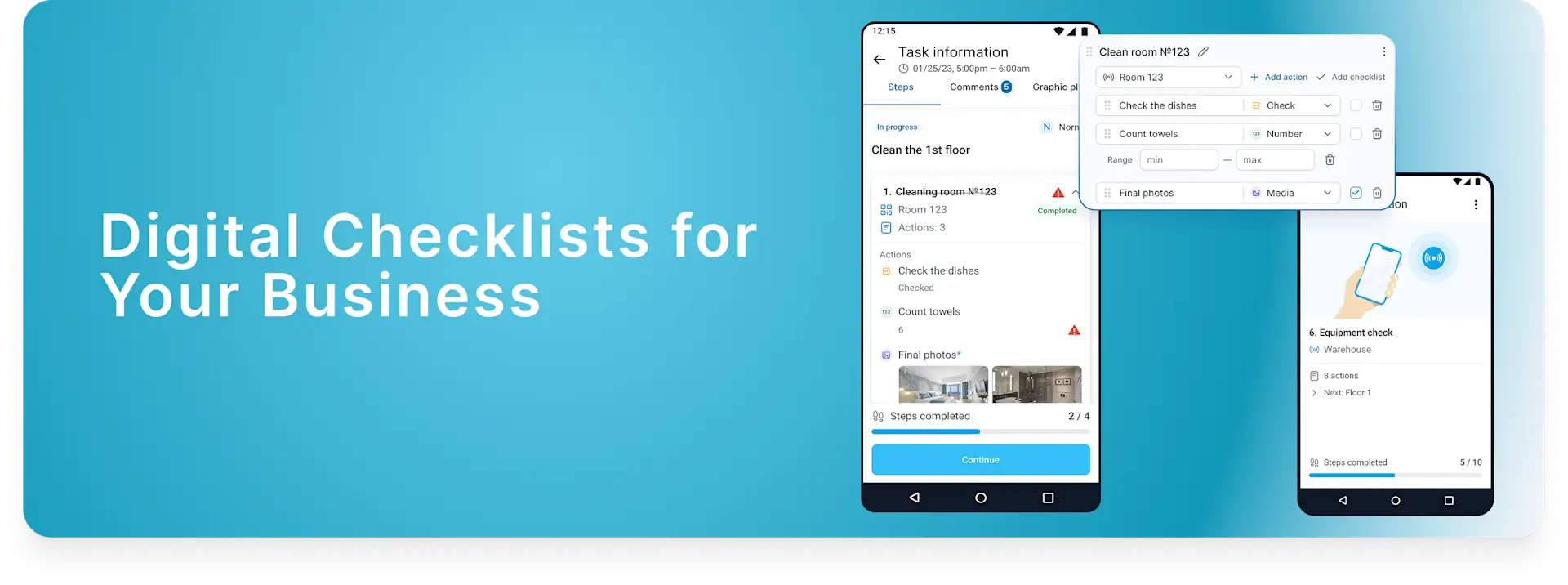
QR, GPS, and NFC Location Tracking for Security Patrols
QR, GPS, or RFID Check-Ins?
In today’s security landscape, technology plays a critical role in streamlining operations, increasing accountability, and improving the efficiency of task management. One of the key features of modern task management software is the ability to track and verify employees locations through various check-in methods, such as QR codes, NFC tags, and GPS tracking. Each of these methods offers unique advantages, depending on the specific needs of your operations.
In this blog post, we’ll explore the differences between QR, NFC, and GPS check-ins in task management software, and how each one can enhance the security of your operations.
In our On-Site Task Management Software, we will refer to “Check-In” across various areas, including security guards, cleaners, audit inspections, maintenance engineers, and more.
QR Code Check-In
QR codes (Quick Response codes) are two-dimensional barcodes that store information, such as a unique identifier or location details. These codes are placed at key checkpoints within a task route, and employees use their mobile devices to scan the QR code when they arrive at a location. The scan logs their presence and time, verifying that they completed the assigned task at the specified location.
Advantages:
Cost-Effective: QR codes are easy and inexpensive to generate, print, and place at various locations.
Quick Setup: They can be placed anywhere within the task area and require no special hardware.
Works Offline: QR code scanning can still function without an internet connection, syncing data when the device reconnects to a network.
Flexible Use: QR codes can be placed on walls, gates, or objects, making them versatile for different environments.
Limitations:
Requires Scanning: Employees must physically scan the QR code, so it’s not as automatic as other options.
Easily Damaged: QR codes can be susceptible to wear and tear, especially in outdoor environments, potentially impacting scan accuracy.
Best for:
Smaller sites or indoor facilities where setup costs and simplicity are priorities.
NFC (RFID) Check-In
NFC (Near Field Communication) technology involves the use of small, embedded tags that store information. When employees approach an NFC tag with an NFC-enabled mobile device, they can tap the tag to check in at that location. The check-in process is automatic and wireless, with no need for scanning.

Advantages:
Quick and Easy Check-In: NFC allows for faster check-ins as employees only need to tap their mobile devices to the tag, eliminating the need for manual scanning.
Durable and Long-Lasting: RFID tags are compact and more durable than QR codes, making them suitable for long-term use in a variety of environments, including harsh outdoor conditions.
More Secure: RFID tags are harder to tamper with or duplicate, offering a more secure method of check-in compared to QR codes.
Limitations:
Short Range: NFC works only when the mobile device is within close proximity (a few centimeters) to the tag, so it’s not suitable for long-range tracking.
Requires NFC-Enabled Devices: Both the mobile device and the tag must support NFC technology, which may limit compatibility with older devices.
Best Use Case:
NFC check-ins are well-suited for larger, outdoor environments where durability and ease of use are critical, such as industrial facilities or construction sites.
Bluetooth Check-In
Bluetooth-based check-ins rely on Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) beacons installed at various checkpoints. These beacons emit a signal that is picked up by employees’ mobile devices when they come within range. Check-ins happen automatically, without the need for employees to actively engage with the system.
Advantages:
Hands-Free Check-In: Bluetooth beacons enable completely automatic check-ins, with employees only needing to be within range of the beacon (typically up to 100 meters).
Efficient in Large Areas: Bluetooth beacons can cover large areas and multiple checkpoints simultaneously, reducing the need for physical interaction and making it suitable for wide-open spaces.
Real-Time Monitoring: The system can provide real-time location tracking as employees move between beacons, giving managers continuous visibility into their team’s movements.
Limitations:
Higher Cost: Bluetooth beacons are more expensive than QR codes and NFC tags, both in terms of hardware and setup.
Battery Usage: Frequent Bluetooth use can drain the battery on mobile devices more quickly compared to QR or NFC systems.
Signal Interference: Beacons may experience signal interference in certain environments, which could affect the accuracy of check-ins.
Best Use Case:
Bluetooth check-ins are perfect for large-scale facilities, campuses, or outdoor tasks where hands-free, long-range tracking is necessary.
GPS Check-In
GPS (Global Positioning System) check-ins rely on satellite signals to track an employee's location in real-time. Employees don’t need to interact with any physical checkpoints; instead, their location is logged automatically based on their GPS coordinates. Managers can monitor employee movements continuously via their mobile devices.
Advantages:
Hands-Free and Automatic: GPS allows for completely hands-free check-ins, with the system automatically logging the employee’s location without requiring any interaction.
Real-Time Location Tracking: GPS provides real-time tracking, allowing managers to see where employees are at any given moment.
Widespread Coverage: GPS is ideal for covering large areas, such as parks, campuses, or industrial zones, without the need for physical checkpoints.
Limitations:
Battery Drain: Continuous GPS tracking can significantly drain the battery on mobile devices, particularly during long shifts.
Indoor Limitations: GPS is less accurate indoors or in densely built-up areas, where satellite signals may be obstructed.
Privacy Concerns: Some employees may feel uncomfortable with constant location tracking throughout their entire shift.
Best Use Case:
GPS check-ins are best suited for outdoor or large-scale environments, such as campuses, construction sites, or parks, where real-time location tracking is essential.

Which Check-In Method is Right for Your Needs?
Choosing the right check-in method depends on the unique needs of your operation. Here’s a quick summary to help guide your decision:
QR Codes: Ideal for small or indoor environments where budget is a concern, and employees can manually scan checkpoints.
NFC: Suitable for environments that require fast, secure, and durable check-in methods, especially in outdoor or industrial settings.
Bluetooth: Best for large facilities or areas that need hands-free, automatic check-ins, covering multiple locations with a single setup.
GPS: Perfect for wide-open spaces where real-time tracking is essential, but may face challenges in indoor settings or areas with limited satellite coverage.
QR codes, NFC tags, Bluetooth beacons, and GPS tracking each offer unique advantages depending on the specific needs of your task management software. By leveraging the right technology, security managers can ensure more accurate tracking, improved accountability, and enhanced operational efficiency.
TARGPatrol try free
TARGPatrol offers a comprehensive solution that integrates all these check-in methods, providing the flexibility to choose the best option for your security operation. Whether you need hands-free GPS tracking for large outdoor areas or cost-effective QR codes for smaller sites, TARGPatrol has you covered. Get started for free: TARGPatrol.